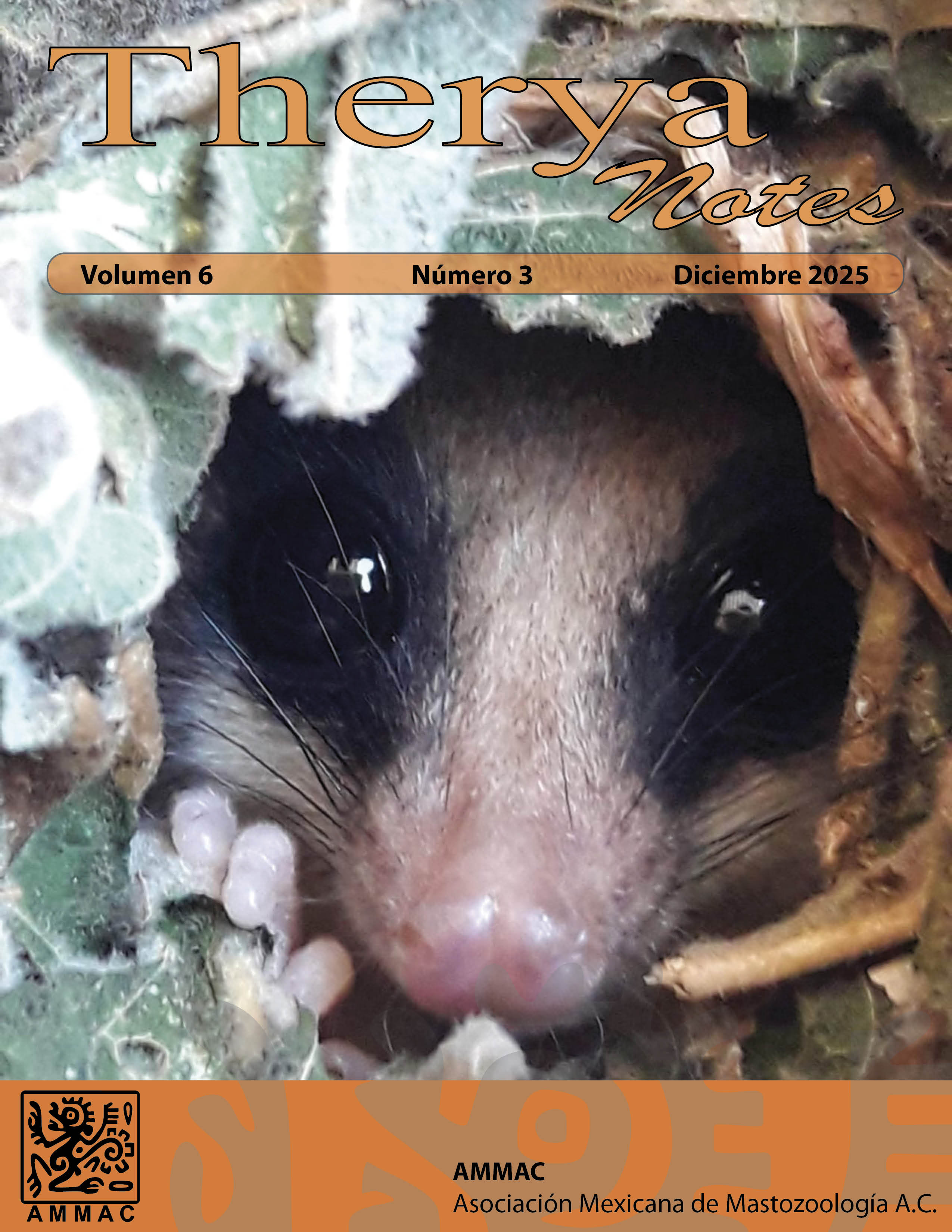
First record of alopecia in Artibeus jamaicensis and Choeronycteris mexicana (Chiroptera: Phyllostomidae) in Puebla, Mexico
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.12933/therya_notes-24-211Keywords:
frugivore, loss of hair, nectarivore, PhyllostomidaeAbstract
Alopecia refers to partial or total hair loss in mammals. It is an autoimmune disease that prevents hair follicle growth and causes hair loss. In this study, we report partial hair loss in three bats: two of the frugivorous species A. jamaicensis and one of the nectarivorous species C. mexicana, collected in the southern area of a protected area in the state of Puebla, Mexico. Bats with alopecia were observed in May and November 2024 during field trips of a project aimed at assessing the conservation status of bat species in the state of Puebla. Bats were captured at a site with low deciduous forest vegetation and mango and banana plantations in Atotonilco, municipality of Huehuetlán el Grande, Puebla. We captured 27 bats of different species. Among them, two adult females of A. jamaicensis without evidence of reproductive activity had partial or total alopecia in the abdominal area. Another individual, an adult male of C. mexicana with scrotal testes, presented with alopecia on the face, neck, and abdomen. This is the first report of alopecia in bats from Puebla, the third for A. jamaicensis in Mexico, and the first for C. mexicana in Mexico. In previous studies on bats in the state of Puebla, there have been no reports of alopecia. Alopecia in these individuals is likely due to environmental stress caused by anthropogenic activities in Atotonilco that probably affect nutritional processes.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Therya Notes

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
THERYA NOTES is based on its open access policy allowing free download of the complete contents of the magazine in digital format. It also authorizes the author to place the article in the format published by the magazine on your personal website, or in an open access repository, distribute copies of the article published in electronic or printed format that the author deems appropriate, and reuse part or whole article in own articles or future books, giving the corresponding credits. The Creative Commons CC BY-NC-SD license is used.![]()